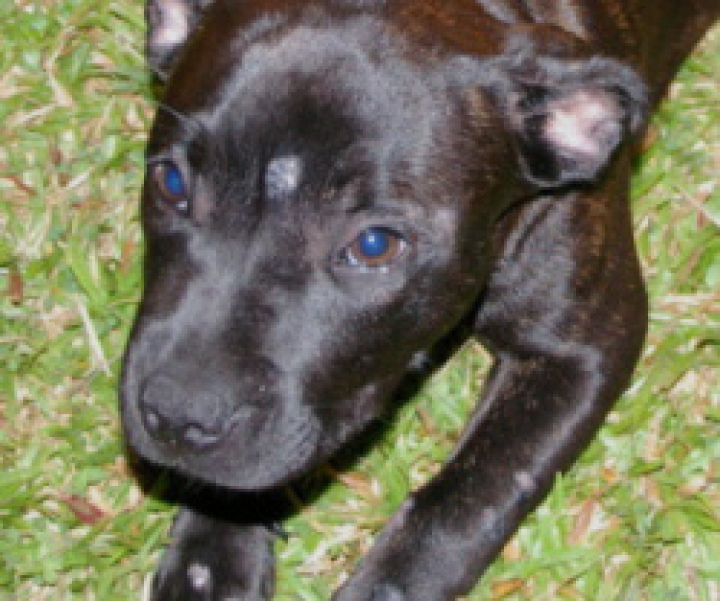
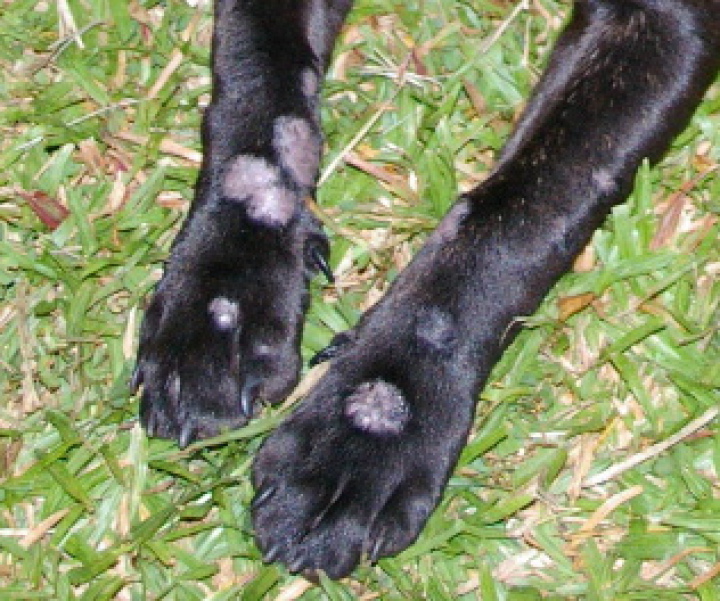
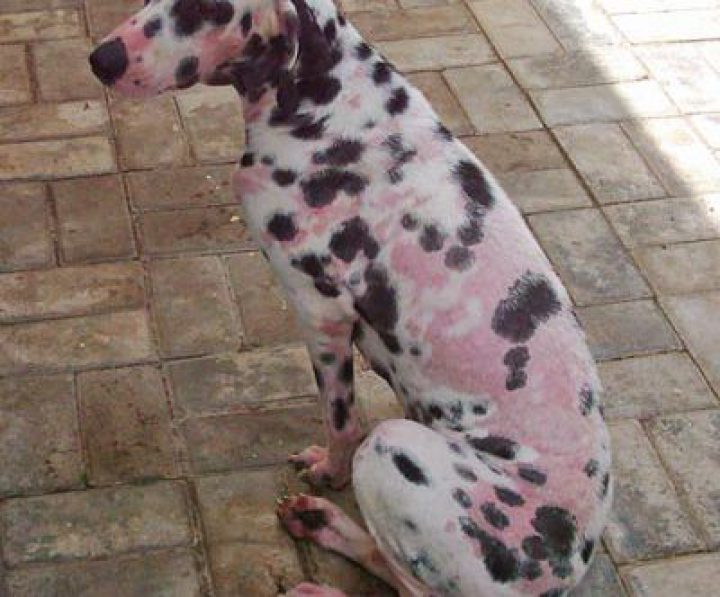
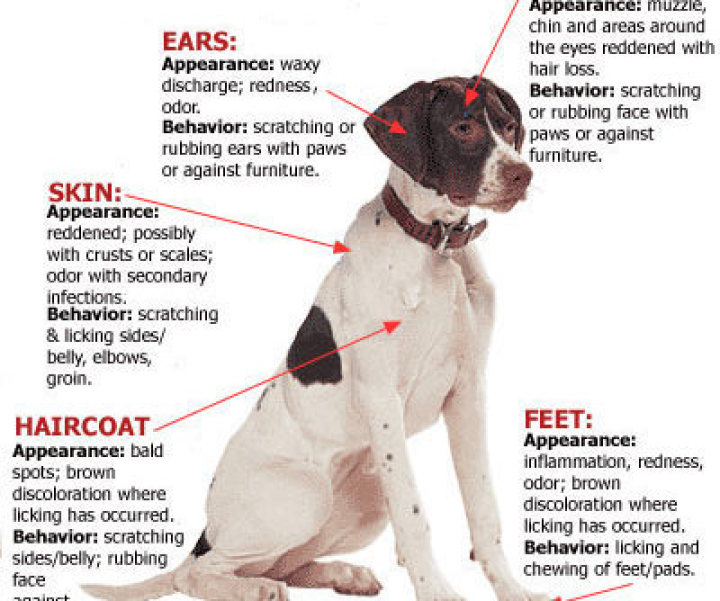
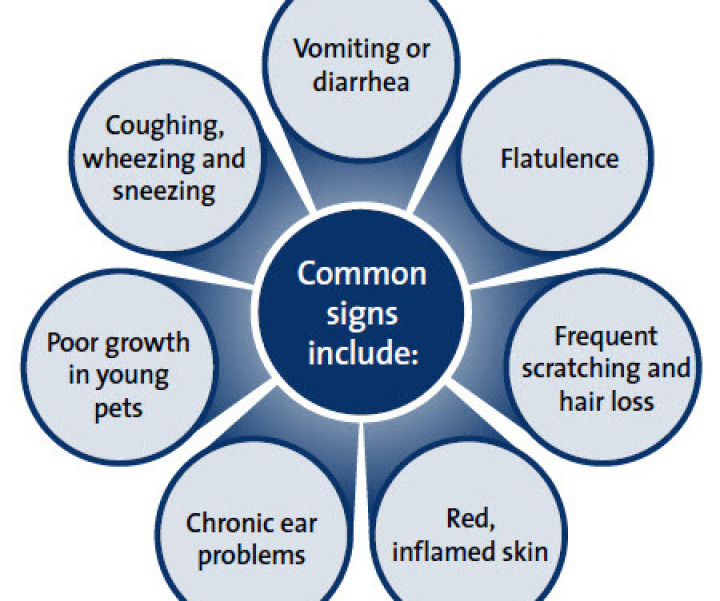
These are common sings of Ring Worms
Seek a local veterinary office
Ringworm can be transmitted by direct contact with an infected animal, or contact with an item that is contaminated with the spores. The spore can be on infected grooming equipment or brushes, in a contaminated boarding facility or kennel, or in the environment where an infected animal has visited. As you can see, because of the spore's ability to survive for long periods in the environment, your dog can contract ringworm just about anywhere other dogs or cats have been. Fortunately, most healthy adult dogs have some resistance to ringworm and never develop symptoms from the fungus. Young dogs are most often infected. Dogs with a suppressed immune system from other diseases or overuse of steroids are also more susceptible to contracting the disease.
Most small, isolated lesions on healthy dogs and puppies will heal on their own within 4 months. In more severe cases, several different treatments are used. For isolated lesions, the area around the lesion should be thoroughly clipped down close to the skin. Care should be taken when clipping not to irritate the skin, as this may promote spreading of the infection. The lesions can then be treated topically twice a day with an antifungal medication. Popular topical treatments include miconazole cream, Lotrimin cream, or 1% chlorhexidine ointment. For more severe or more generalized lesions, in addition to clipping and topical treatment, antifungal shampoos or dips can also be beneficial. A 0.5% chlorhexidine shampoo, 2% miconazole shampoo, ketoconazole shampoo, lime sulfur dips, or 2% chlorhexidine solution that are applied every 2 to 4 days have all been used effectively.
Another treatment option is to use oral antifungal agents. Historically, griseofulvin was the drug of choice. Ketoconazole, and most recently itraconazole, have been used successfully. These products all have to be given for several months, and because of their potential toxicity, must only be used under close direct veterinary supervision. Griseofulvin should not be used in breeding or pregnant animals.
ZOONOTIC DISEASE
Yes. Ringworm can be transmitted between dogs and people. Persons with suppressed immune systems, such as those with HIV infections or AIDS, and those undergoing chemotherapy may be especially vulnerable. Persons should wear gloves when handling affected animals and wash hands well afterwards.